Introduction
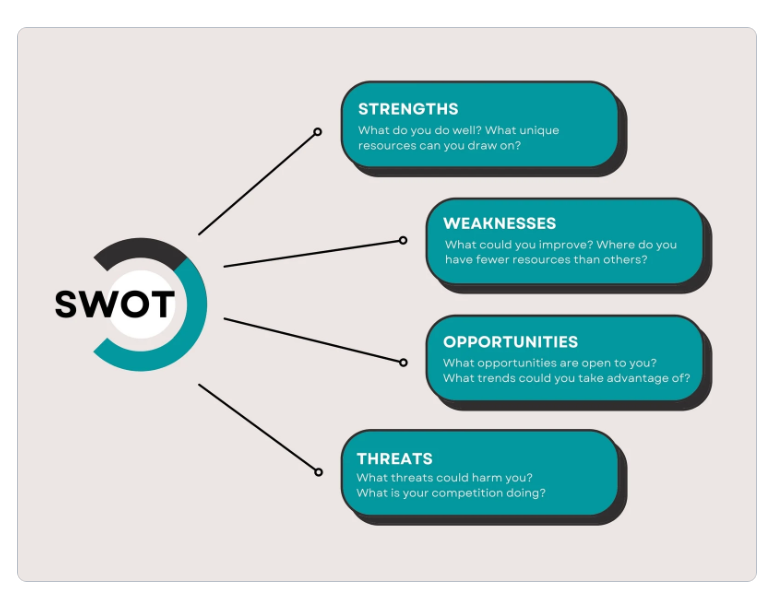
A SWOT analysis is a strategic management tool used by SMEs to understand their internal capabilities (Strengths and Weaknesses) and external environment (Opportunities and Threats). This analysis provides valuable insights for strategic planning and decision-making.
By conducting a thorough SWOT analysis, SMEs can gain a clear understanding of their position in the market, identify areas for improvement, and develop effective strategies to achieve their goals. This lecture is particularly designed for History and Diplomatic students and practitioners.
Understanding SWOT
- Strengths: Internal attributes that give your business an advantage.
- Weaknesses: Internal limitations that hinder your business’s performance.
- Opportunities: External factors that your business can leverage.
- Threats: External factors that could harm your business.
Steps in Conducting SWOT Analysis
1. Gather Information:
- Internal Assessment:
- Core competencies
- Financial resources
- Human resources
- Technology
- Brand reputation
- Operational efficiency
- Intellectual property
- External Assessment:
- Market trends
- Economic conditions
- Competitive landscape
- Technological advancements
- Regulatory environment
- Customer needs and preferences
2. Identify SWOT Factors:
- Strengths: What are your business’s unique selling points? What do you do better than your competitors?
- Weaknesses: What are your business’s limitations? What areas do you need to improve?
- Opportunities: What external factors can you exploit? What new markets or products can you enter?
- Threats: What external factors could harm your business? What challenges do you face?
3. Prioritize:
- Rank the factors in each category based on their impact on your business.
- Focus on the most critical strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
4. Analyze and Develop Strategies:
- Identify how to leverage strengths and opportunities.
- Develop strategies to address weaknesses and threats.
- Consider how to match your strengths with external opportunities.
- Develop contingency plans for potential threats.
Tips for Effective SWOT Analysis
- Involve key stakeholders in the process.
- Be honest and realistic.
- Use both quantitative and qualitative data.
- Regularly review and update the analysis.
- Focus on actionable insights.
Example SWOT Analysis for A small bakery
Strengths:
- High-quality, fresh products
- Strong local reputation
- Experienced bakers
- Loyal customer base
Weaknesses:
- Limited product range
- Small production capacity
- Dependence on local market
- Lack of online presence
Opportunities:
- Growing demand for organic and healthy baked goods
- Expanding to new customer segments (e.g., corporate clients)
- Online ordering and delivery
- Partnerships with local cafes and restaurants
Threats:
- Increasing competition from large bakeries
- Rising costs of raw materials
- Economic downturn
- Changes in consumer preferences
Example SWOT Analysis for a Small Retail Store
Strengths:
- Strong customer relationships
- Prime location
- Knowledgeable staff
- Unique product selection
Weaknesses:
- Limited marketing budget
- Small store size
- Dependence on a few key suppliers
- Lack of online presence
Opportunities:
- Growing online shopping trend
- Expanding product line
- Partnership with local businesses
- New customer segments
Threats:
- Economic downturn
- Increasing competition
- Supply chain disruptions
- Changes in consumer preferences
